Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) encompasses a set of inflammatory diseases of the upper female genital tract: uterus, tubes, and ovaries. It affects young women around the age of 20 to 35
It is the most common and most serious complication of sexually transmitted disease, causing high rates of ectopic pregnancy (outside the uterus), chronic pelvic pain, and infertility.
How do I acquire DIP?
The most common cause is sexual transmission, but it can also arise after gynecological procedures or events, such as:
- childbirth
- abortion
- insertion of an IUD (intrauterine device) for contraception,
- endometrial biopsy
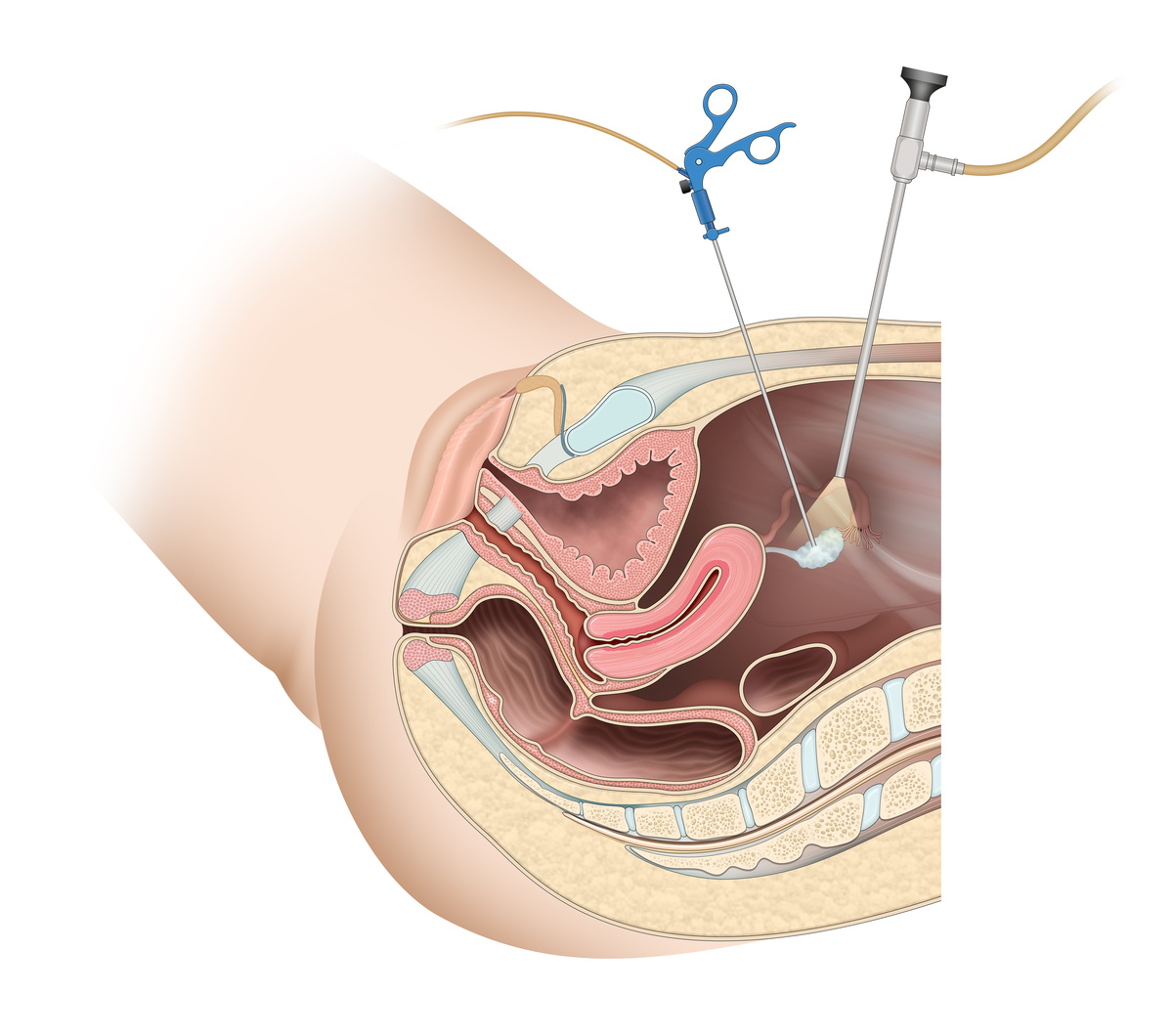
- hysteroscopy
- uterine curettage
The bacteria most frequently involved in PID are Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhea. However, bacteria from the normal vaginal flora may be present.
What does it feel like?
The most common symptoms are:
Vaginal discharge (leucorrhoea), usually with altered color, odor, and consistency, and lower abdominal pain. Shouldn’t it have a separate highlight since it is the main symptom? That starts right after the menstrual period.
Fever, chills, pain during sexual intercourse, or irregular menstrual bleeding may occur. It is essential to differentiate from other diseases that cause similar symptoms, such as acute appendicitis and ectopic pregnancy.
How does the doctor make the diagnosis?
Diagnosis includes physical examination, which determines the presence and characteristics of discharge, pain on abdominal palpation pain on palpation, and mobilization of the uterus. Several laboratory tests, including blood count, pregnancy test (hCG), chlamydia and gonococcus research, EQU, a fresh examination of vaginal contents, as well as pelvic ultrasound, contribute to confirming the diagnosis.
How is PID treated?
Treatment of uncomplicated PID should be done on an outpatient basis, using antibiotics and regular patient monitoring.
Complicated PID requires hospitalization and intravenous antibiotic therapy followed by oral supplementation.
The sexual partner must always be treated.
Prevention
Prevention includes the need for safe sexual behavior, encouraging the use of condoms, and effective contraception.