Embryo
Discover the stages of Embryo development, step by step, of each stage: Egg, Sperm, in the zygote stage, from 2 to 4 cells, from 8 cells, from morula, from the blastocyst, and inside the uterus.
An egg
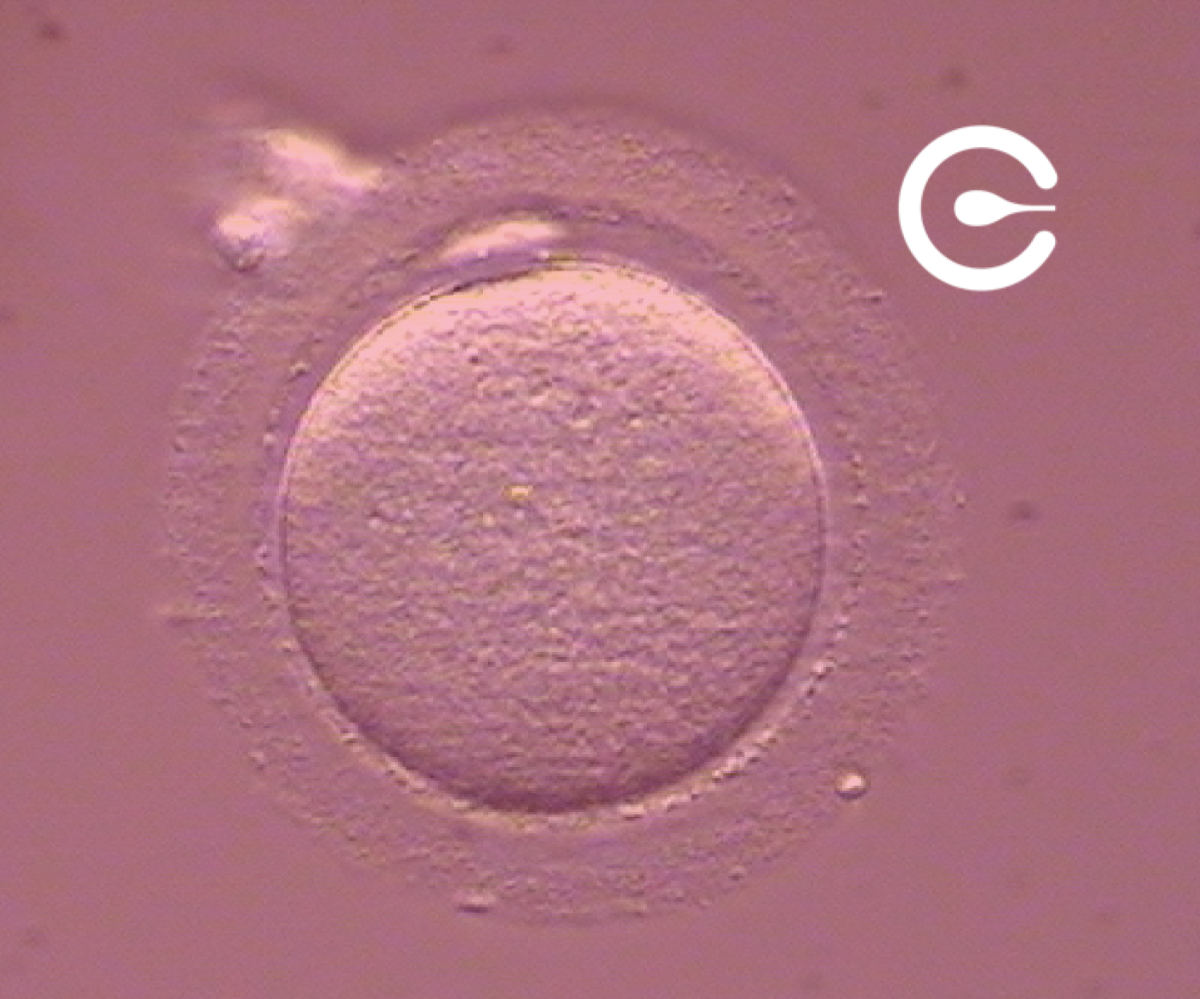
The egg is a female reproductive cell and the largest cell in the organism. It forms in a woman’s ovary during fetal development. Once developed, menstrual cycles occur, and every month, one or more eggs grow and mature.
Sperm
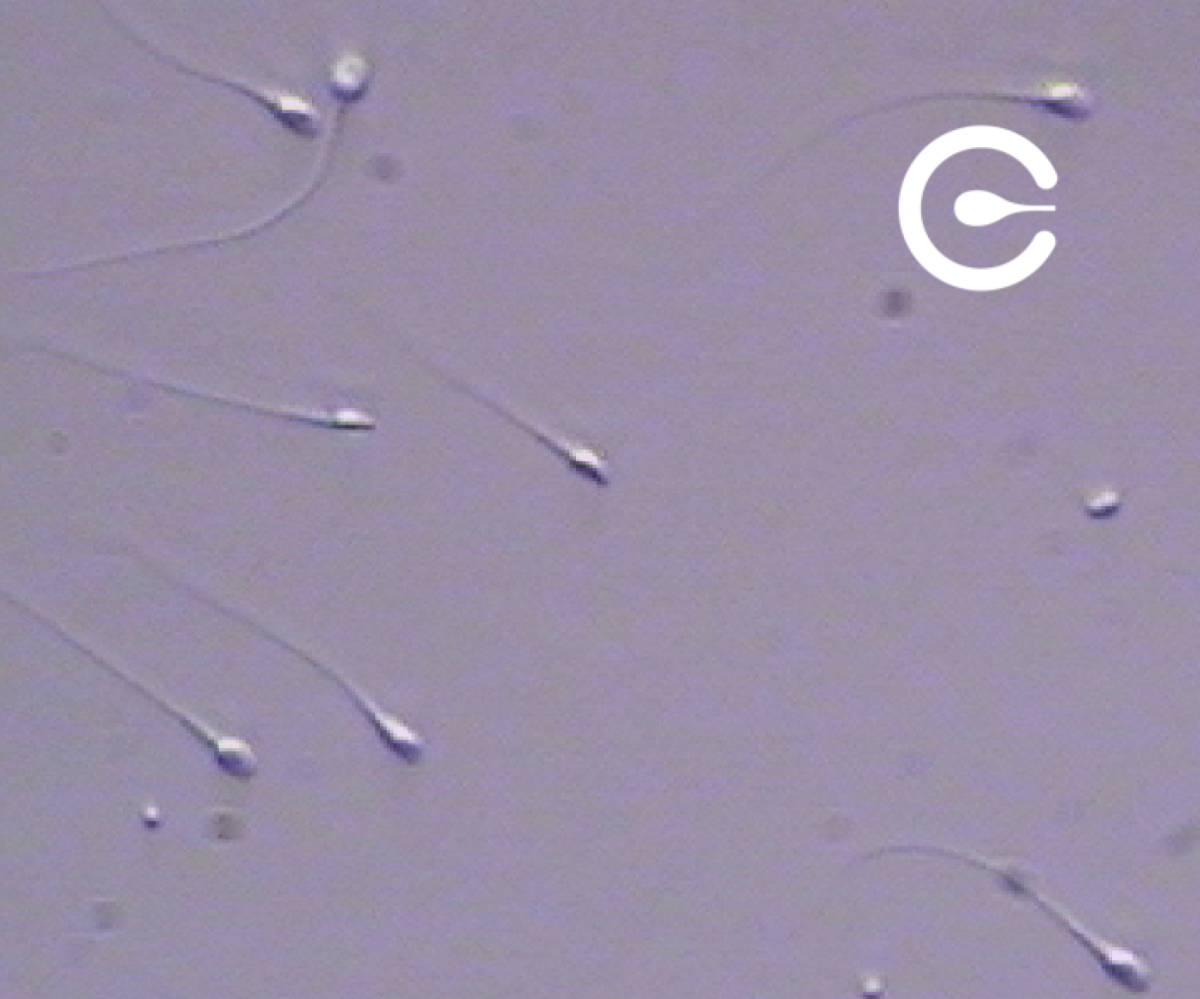
Human sperm is the male reproductive cell. It is small and elongated and is produced in the man’s testicles. Its function is to promote reproduction, penetrate the egg, and fertilize it.
Fertilized embryo at the zygote stage
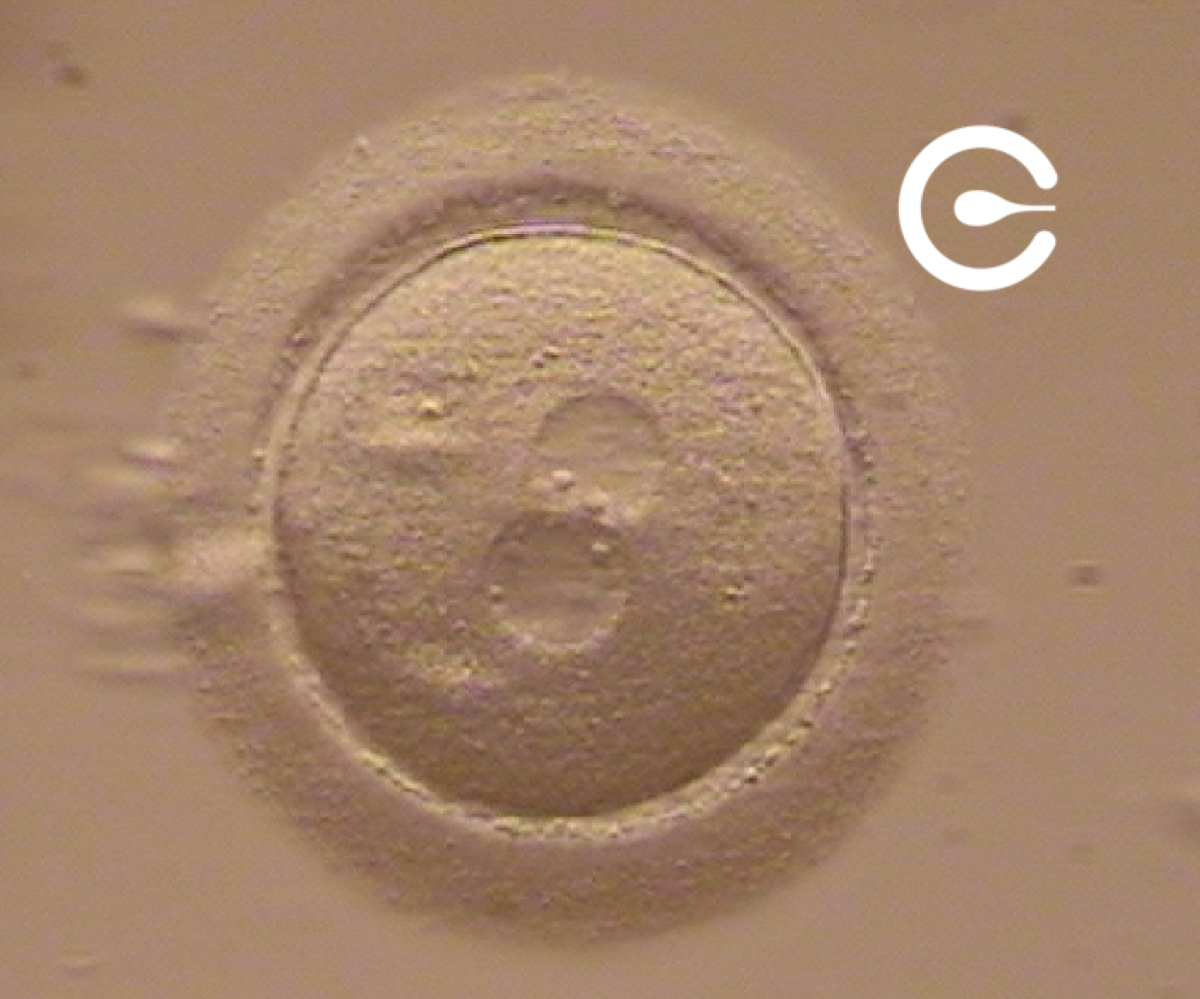
Fusing the egg with the sperm gives rise to the zygote, the first stage of an embryo. A zygote is characterized by the presence of two pronuclei, male and female. The pronuclei contain the genetic material from the father and mother that will be transmitted to the embryo.
2 to 4 cell embryo (2nd day)
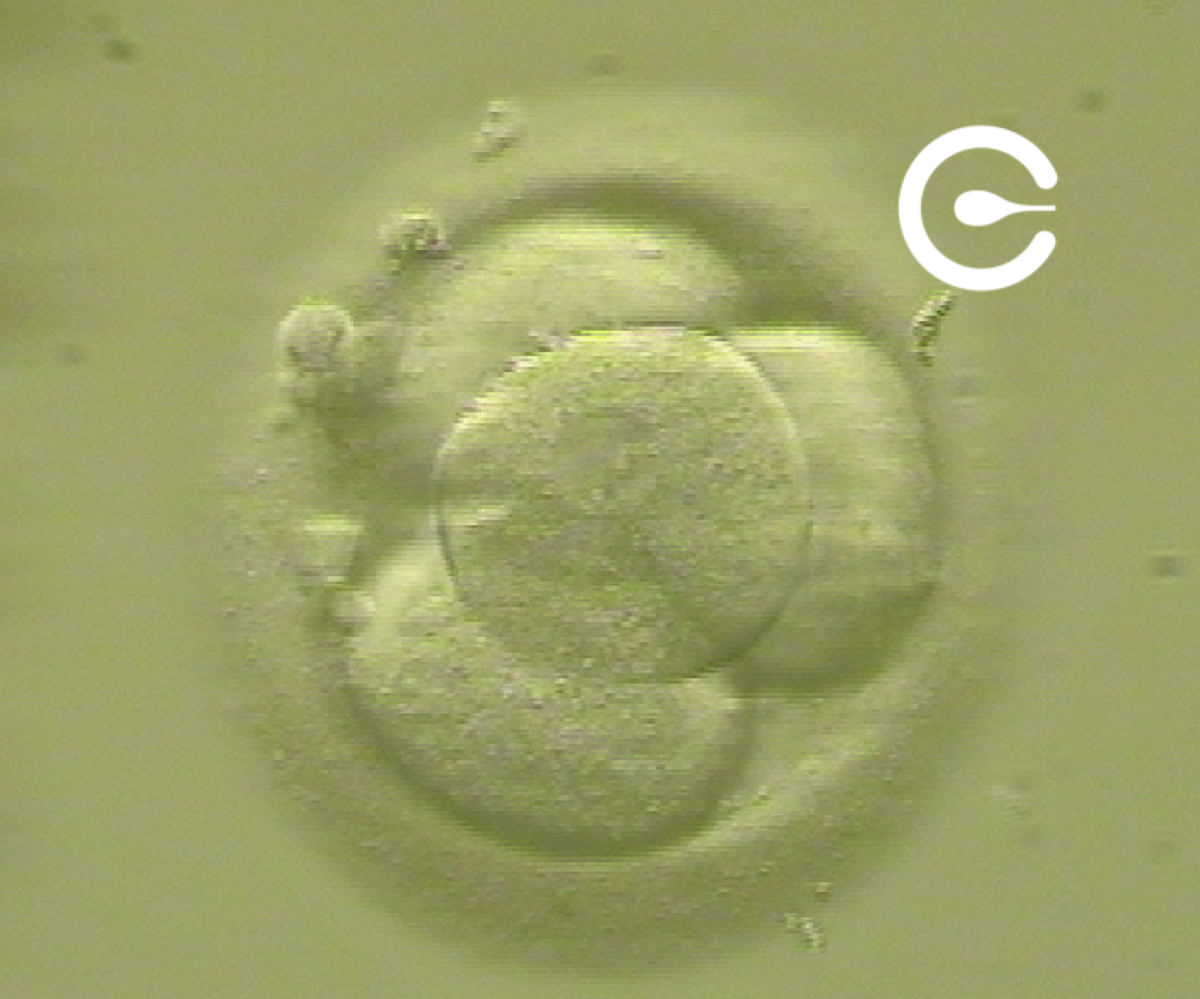
Cell division of the zygote begins. First, into two cells, each cell divides more times, and the embryo grows.
8-cell embryo (3rd day)
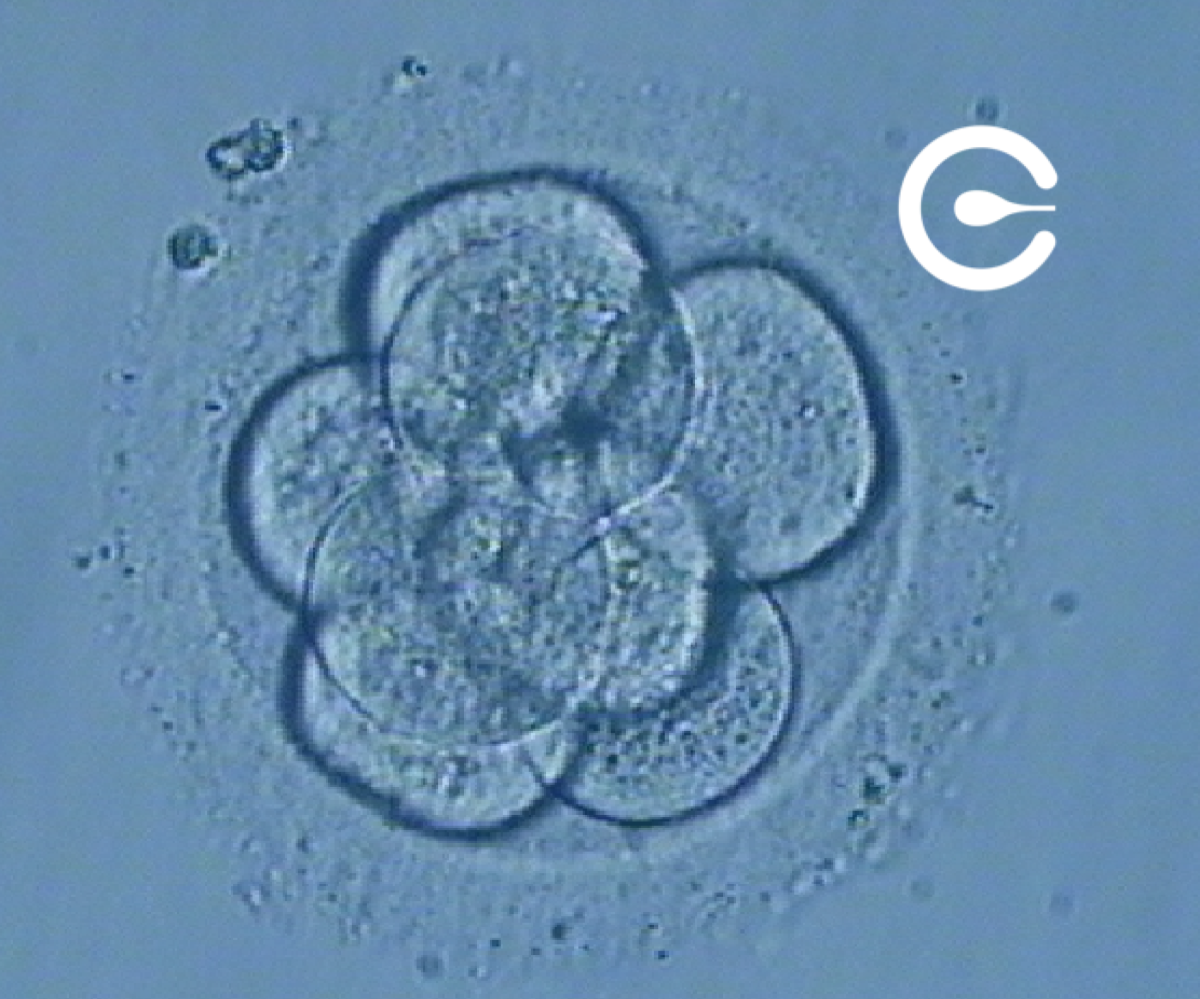
Cell divisions continue until approximately eight cells are reached. On that day, the quality of the embryos is assessed, as not all of them develop correctly. The embryos can be transferred to the mother’s uterus or continue to be cultured in the laboratory. The process of cell division in the embryo is called cleavage.
Embryo at the morula stage (4th day)
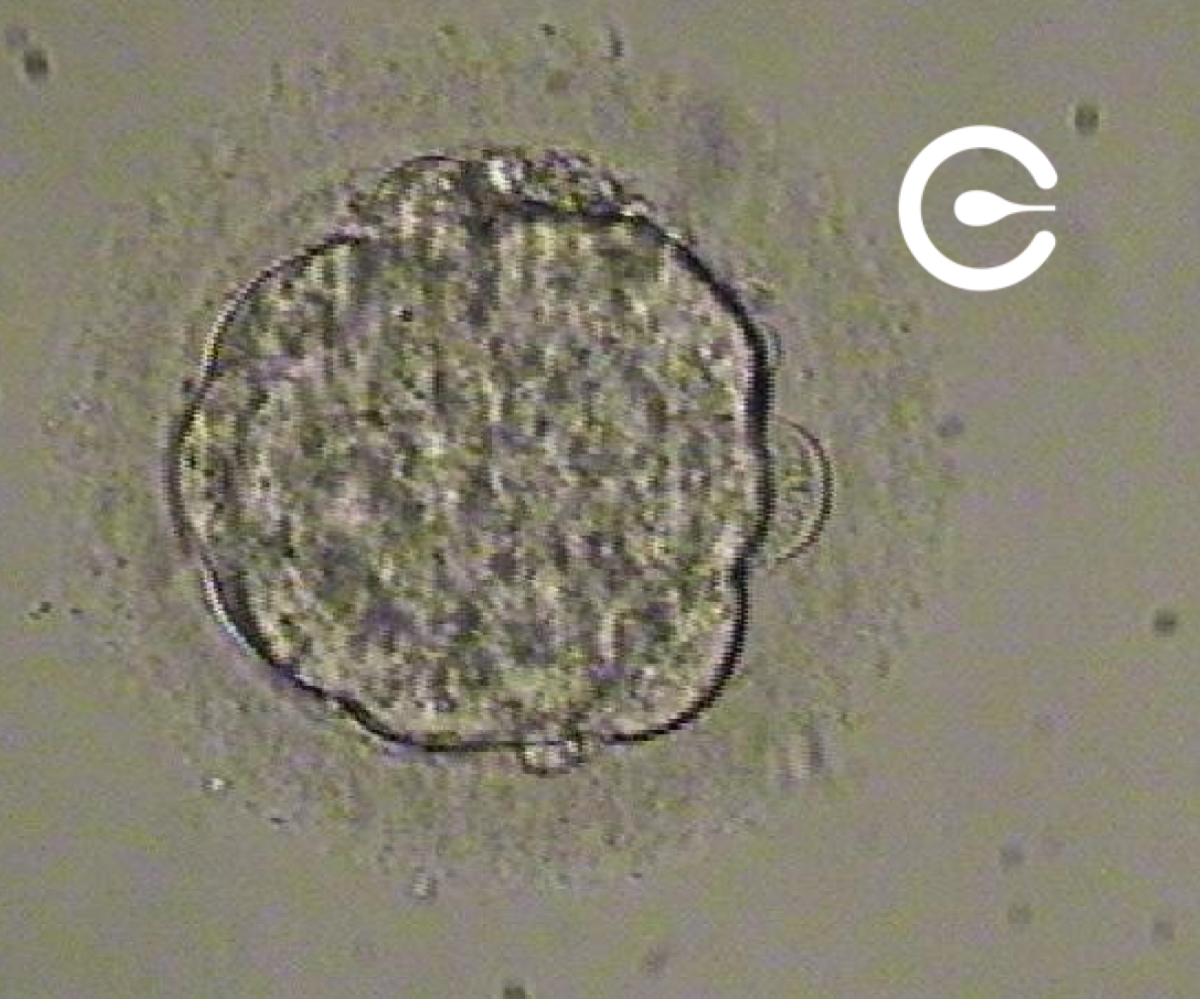
Divisions continue to increase the number of cells, and they compact to form the morula. The name morula is due to the appearance of the embryo, similar to a blackberry. This process of cellular compaction is essential for cells, which until now were multiplying without establishing relationships between them, to begin generating connections that allow the evolution to the next step of embryonic development: the formation of blastocysts.
Embryo at the blastocyst stage (5th day)
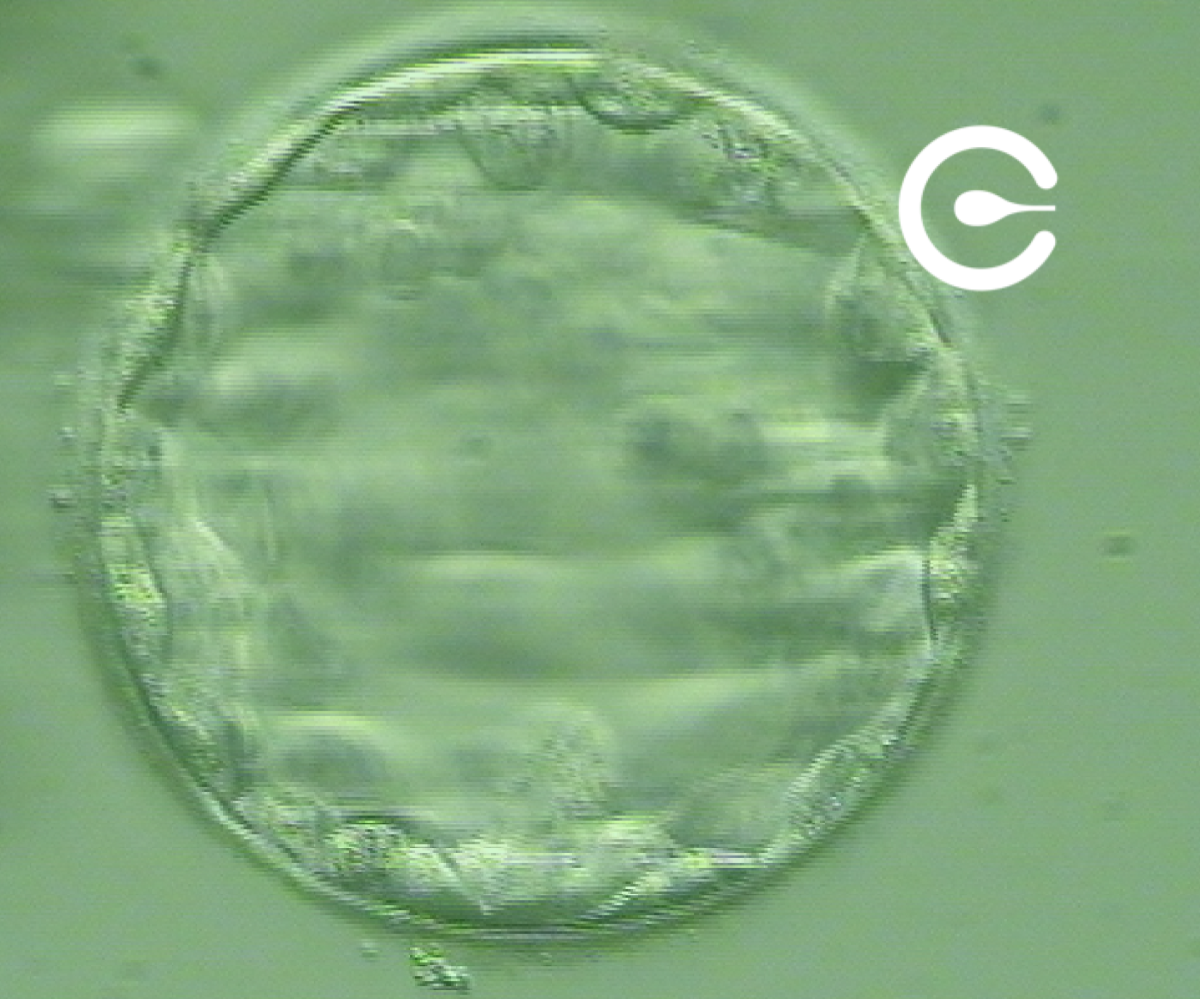
A blastocyst is an embryo that is 5 to 7 days old and comprises dozens of cells. The blastocyst represents the stage of embryonic development before implantation in the mother’s uterus.
*Embryo in the uterus
Inside the uterus, the blastocyst adheres to the endometrium, and implantation occurs through a process known as hatching. In the embryonic period, three main layers are formed: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, which later give rise to their own tissues and organ systems.
* Book NaÎtre
Editora Hachette
Credit for the two photos (embryo in the uterus): Lennart Nilsson